Adopting acceptance tests can be a good strategy to achieve a more consistent and quality-focused software development cycle. However, within an agile context, the time taken to implement these tests must not impact the functionality delivery schedule, while the code architecture must comply with the company’s technical guidelines.
This article demonstrates how StackSpot AI can speed up construction of acceptance tests, bringing more efficiency and code standardization to the project.
What is acceptance testing?
Acceptance testing is a formal description of the expected behavior of a software product, expressed as a usage scenario. A quality control team runs acceptance tests to ensure that the software or application meets business requirements and the end user’s needs.
Acceptance testing allows an organization to involve the business area in the testing process and collect feedback to pass on to the development team. This feedback helps quality control staff to identify flaws that may have gone unnoticed during the development stage tests, such as unit tests.
Moreover, acceptance tests help developers understand the business needs of each feature of the tested software.
What is Acceptance Test-Driven Development (ATDD)?
Acceptance Test-Driven Development (ATDD) is a methodology that includes writing acceptance tests before implementing the corresponding functionality, following the same principle as Test Driven Development (TDD). These tests represent the user’s point of view and act as a form of validation, checking that the system works as intended.
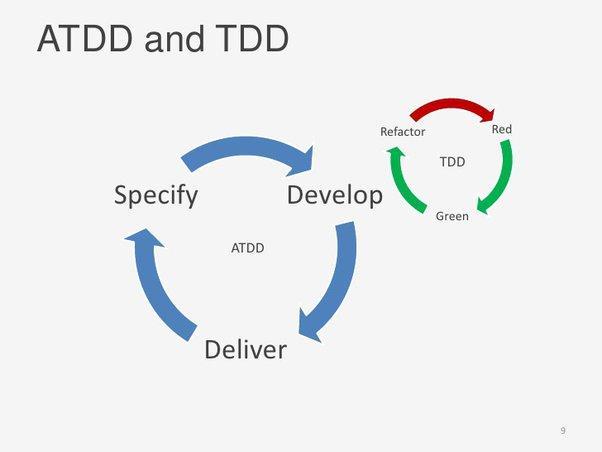
ATDD is a collaborative practice, involving team members with different roles — for example, Product Owners (POs), developers, and QA — collaborating to write acceptance criteria. Subsequently, these criteria will be transformed into acceptance tests to validate the system’s multiple usage scenarios. These tests enter the “Failure – Refactoring – Success” cycle until final delivery.
Main benefits of Acceptance Test-Driven Development (ATDD)
- Early identification of problems: By creating acceptance tests for each requirement or user story, flaws can be spotted earlier in development.
- Reducing rework: As flaws are spotted earlier, rework can be reduced, saving time and resources.
- Understanding requirements: Refining acceptance tests helps an organization to understand and clarify the details of the requirements early on, instead of finding out unclear requirements only halfway through the code.
- Increased test coverage: By focusing on test coverage at the acceptance level, ATDD improves overall test coverage and ensures that critical functionality is thoroughly tested.
- Customer satisfaction: By creating acceptance tests for each requirement or user story, the focus is on customer satisfaction and on meeting their needs.
Definition of Acceptance Criteria
Acceptance Criteria are written while User Stories are created in a partnership between QA and the project’s PO. Scenario writing follows the Gherkin pattern, a standardization technique for writing test specifications based on Behavior-Driven Development (BDD).
| Acceptance Criteria Scenario: 1 – Search for an existing product Given that the user accesses the home page Searches for a current product Then, the search successfully shows the product Scenario: 2 – Search for non-existent product Given that the user accesses the home page When searching for a non-existent product Then, the search shows the following message: “Product not found.” |
The table above outlines two examples of acceptance criteria written in the Gherkin standard, each with three Steps (Given, When, and Then).
Refining with the team
The next step is to refine the acceptance criteria with the team, making sure that all the expected behaviors are mapped out.
- POs review with a business perspective;
- Developers review with a technical perspective, thinking about the architecture that will meet the requirements;
- QAs review with a quality perspective, creating acceptance tests.
Once the refinement is complete and the feature is implemented, it’s time to transform the acceptance criteria into automated tests, which will validate the delivery of the functionality.
Next, find out what StackSpot AI is and how this product can speed up the creation of acceptance tests.
Get to know StackSpot AI
StackSpot AI is a code assistant that uses context (Stack AI) and Knowledge Sources to produce quality code in an assertive manner. Any developer can use natural language to generate code based on the standards defined by the company.
StackSpot AI stores people’s preferences and needs using code and documentation from pre-configured knowledge sources, known as Stack AIs, Knowledge Sources, and Quick Commands:
- Stack AIs – groups of declarative technologies to provide more context to LLM;
- Studios – responsible for grouping Stack AIs according to their purpose;
- Knowledge Sources – allow generation of contextualized code based on pre-registered code snippets and APIs;
- Quick Commands – customized quick commands for code snippets and frequently used actions.
After these definitions, StackSpot AI uses a Large Language Model (LLM) to build highly contextualized code snippets, standardized functions, technical texts, and even automated tests.
Studio
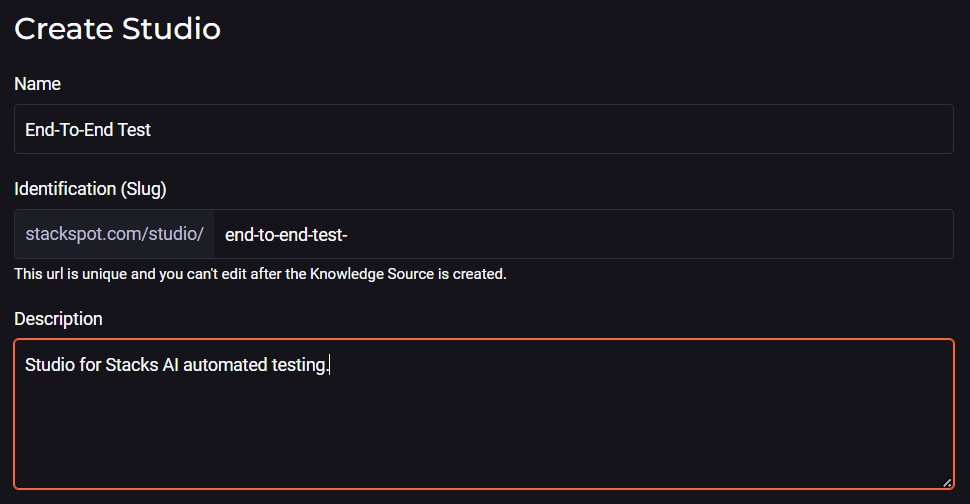
After authenticating, you must create a Studio to store the Stack AI used in the tests, as shown in the example below.
Stack AI
Next, register a Stack AI associated with the newly created Studio. As a practical example, a Stack was created with the following definitions: JavaScript programming language, Cypress framework, and Cucumber BDD for building end-to-end tests.
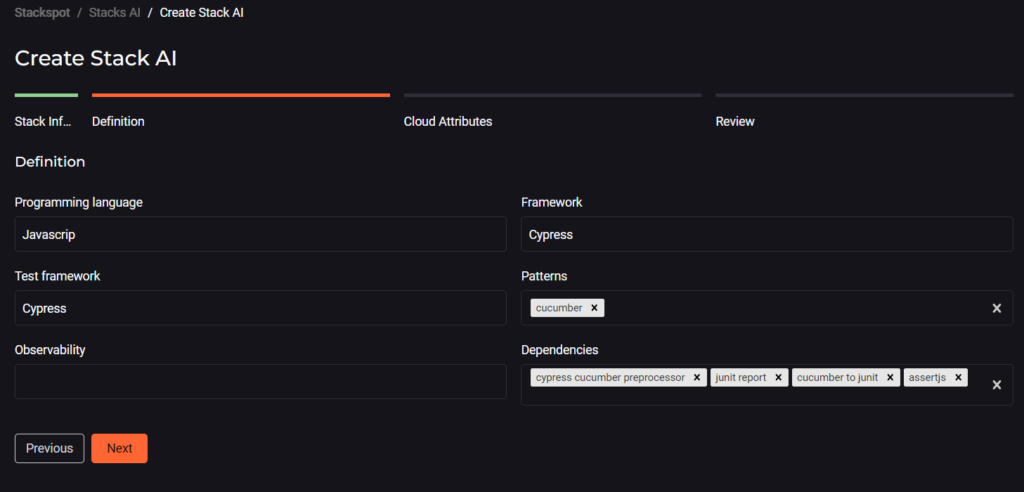
As these are automated tests, the Observability field can be disregarded.
Knowledge Source
The next step is to register a Knowledge Source of the Snippets Group type. Snippets are customized and standardized code snippets, which StackSpot AI will use as a reference to generate contextualized code.
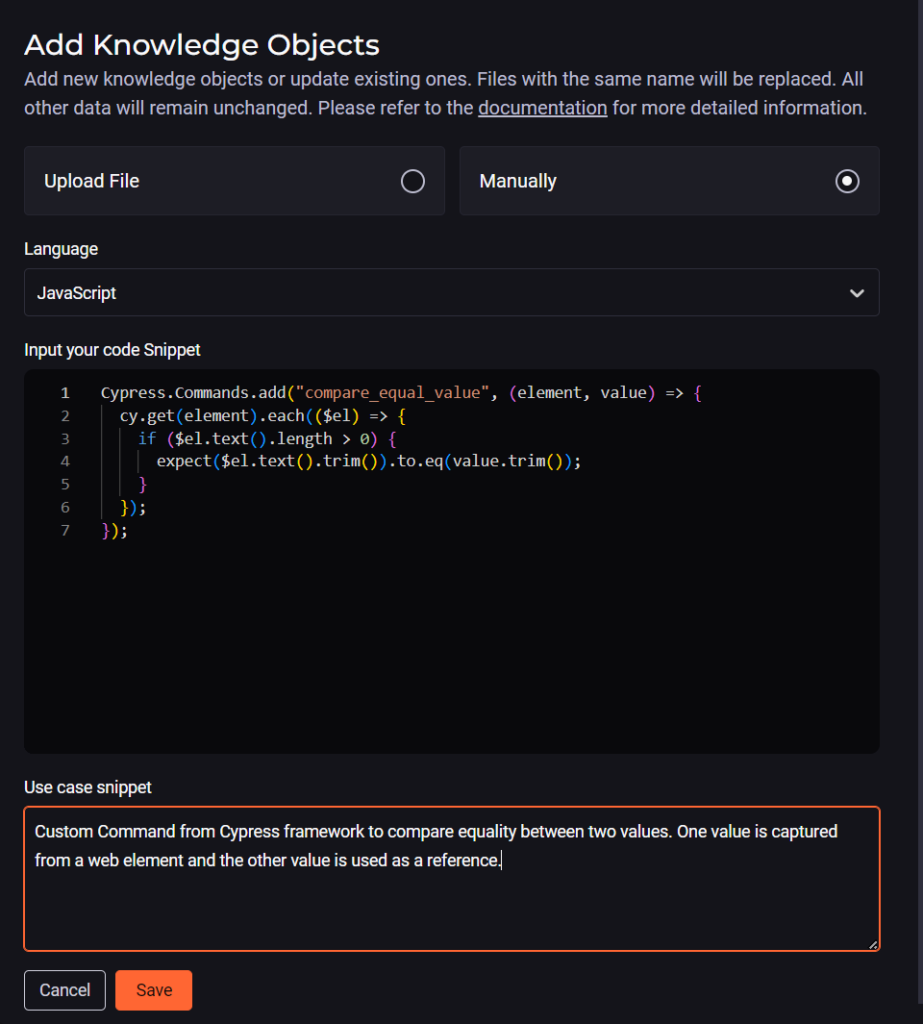
In the example above, a snippet has been created with a Cypress Custom Command that compares two values, in the JavaScript language.
Quick Commands
To provide even more speed to the implementation of the test code, a Custom Quick Command of the Prompt type was created, as shown below.
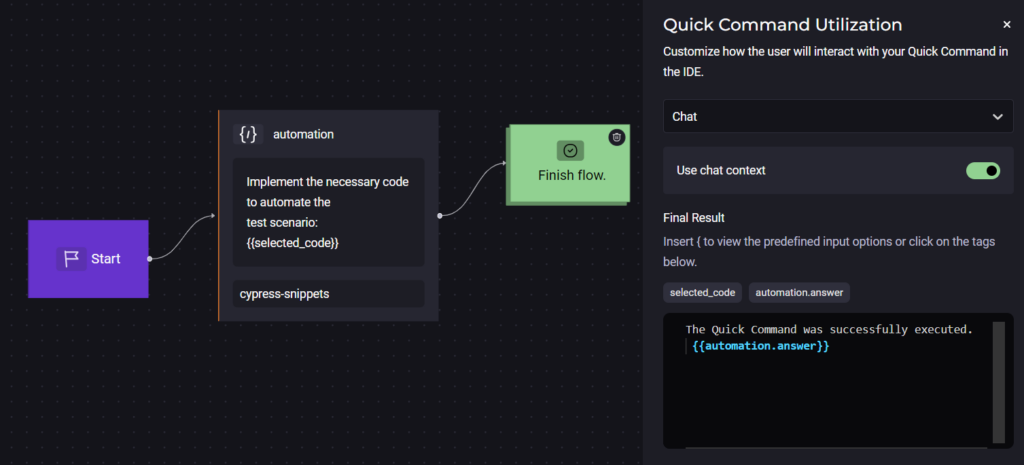
The selected form of interaction was via Chat, so StackSpot AI deposits the result within the conversation itself.
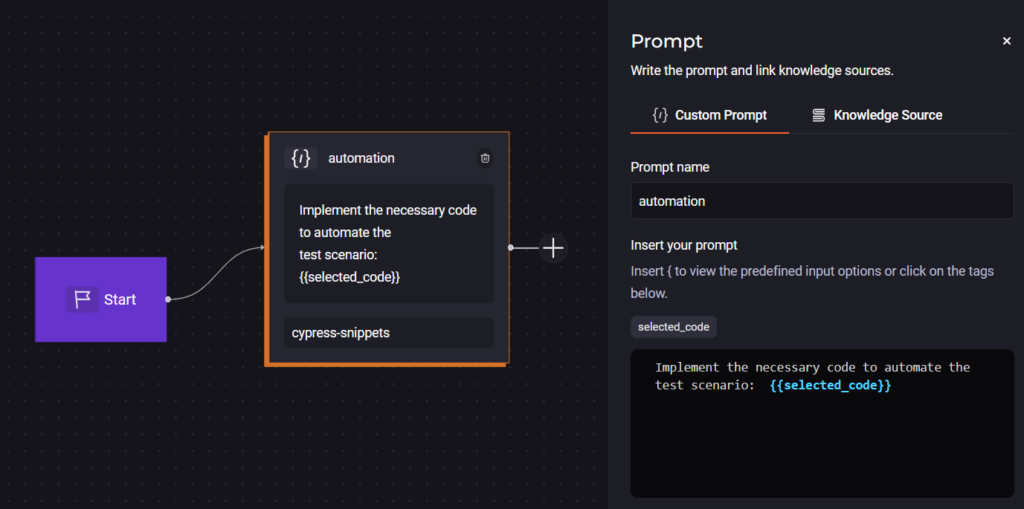
Importantly, the Quick Command must be associated with the Knowledge Source and published in the Studio created earlier.
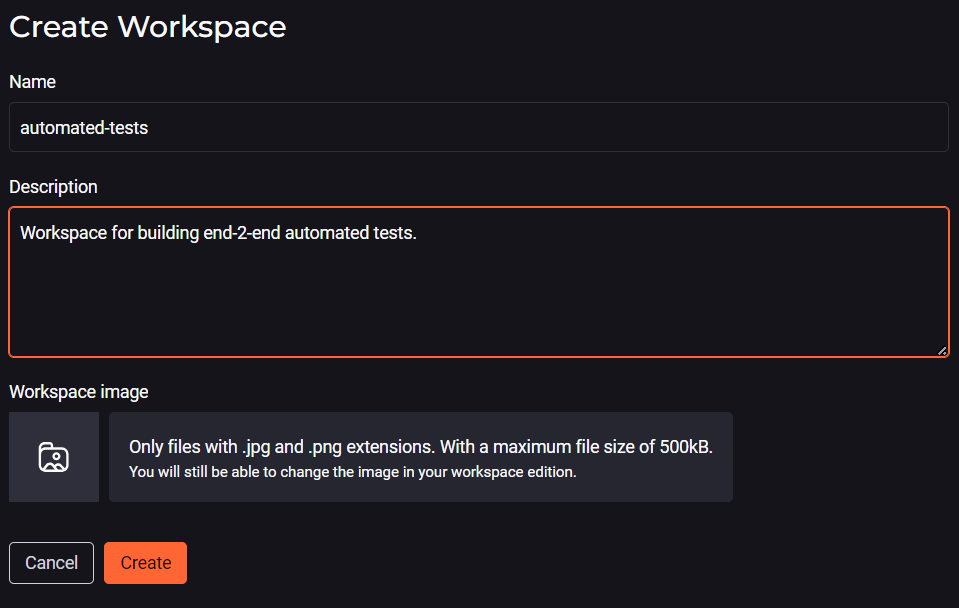
Workspace
Finally, you have to create a Workspace by associating all the artifacts you created earlier with it: Stack AI, Knowledge Sources, and Quick Command.
Implementing acceptance tests with StackSpot AI
StackSpot AI Extension
StackSpot AI provides a plugin to integrate it into the development environment (IDE) in IntelliJ and Visual Studio Code (VS Code). The VS Code extension was installed to apply the proposed example, as shown below.

After installation, log in via your GitHub account and select the Workspace and Stack AI you created earlier.
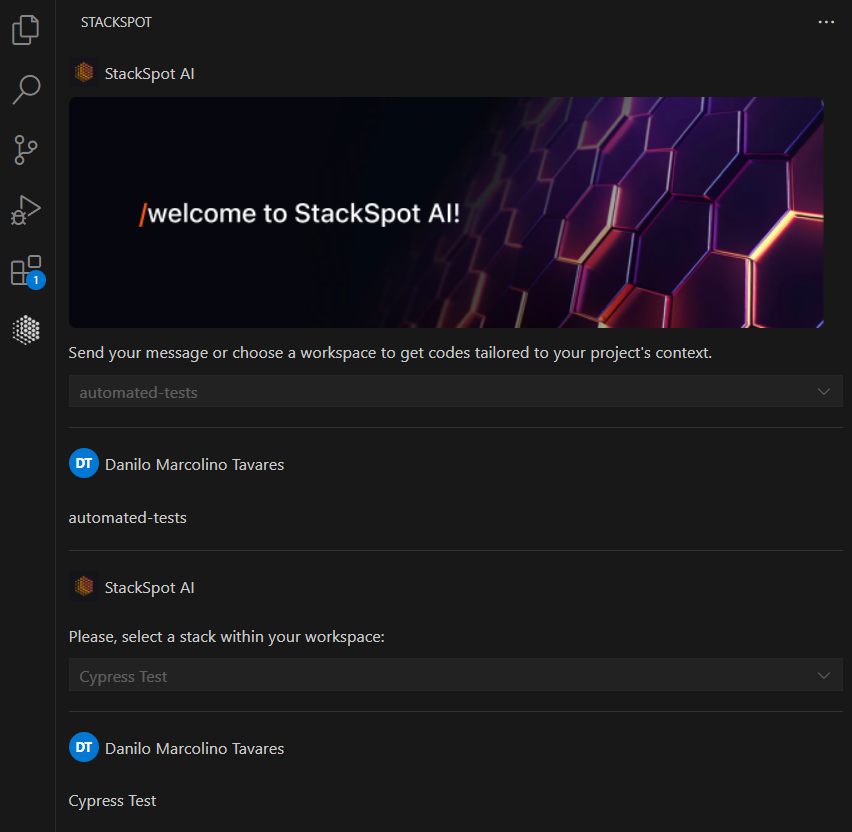
Now add the acceptance criteria to a text file, select, and use the Quick Command created with the right button on the mouse to generate the necessary code.
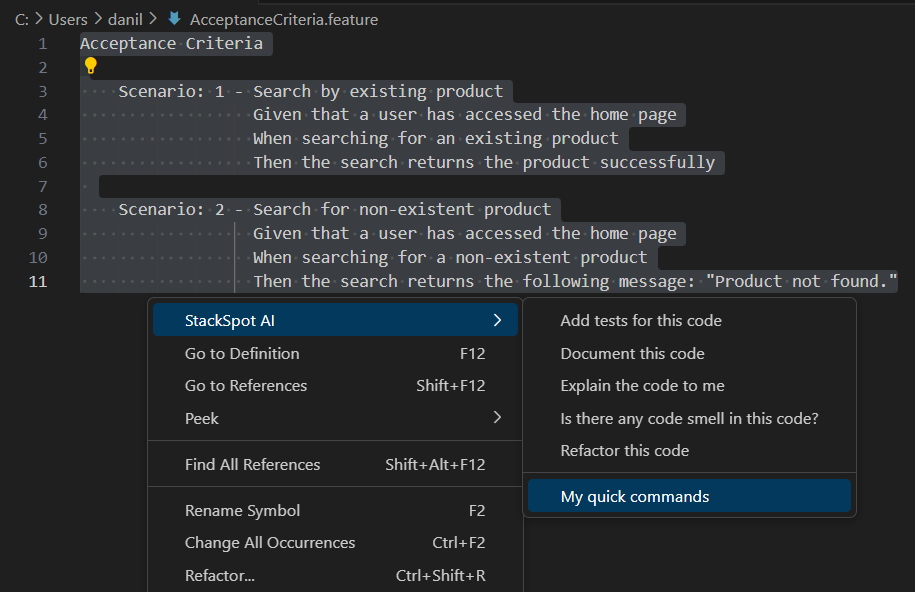
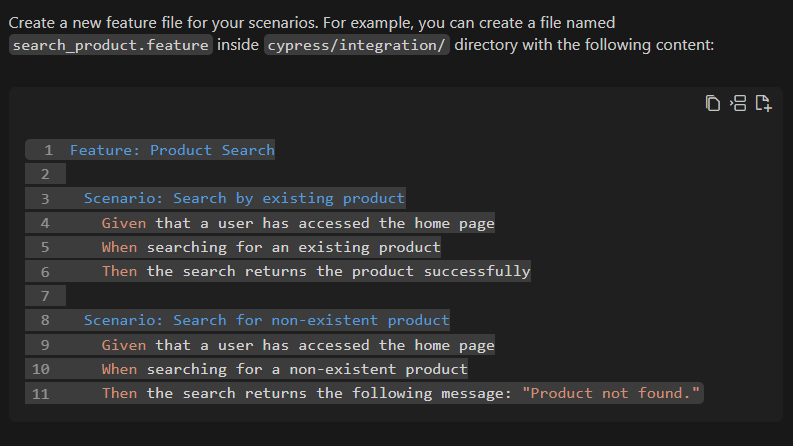
As a result, StackSpot AI first built the feature file with the acceptance tests following the Cucumber standard.
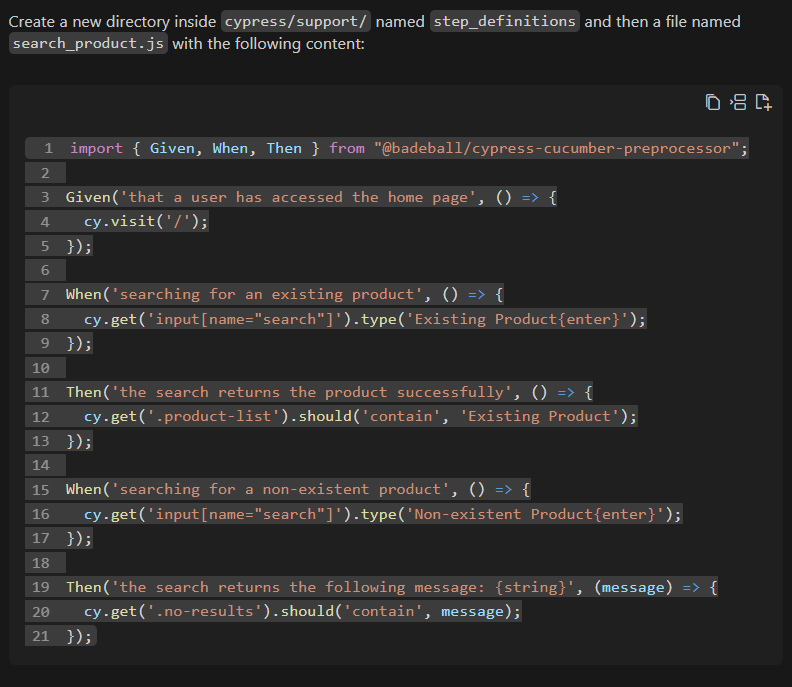
Then, the JavaScript code needed to execute the test steps was delivered, following the standards that had been pre-determined in the Knowledge Source.
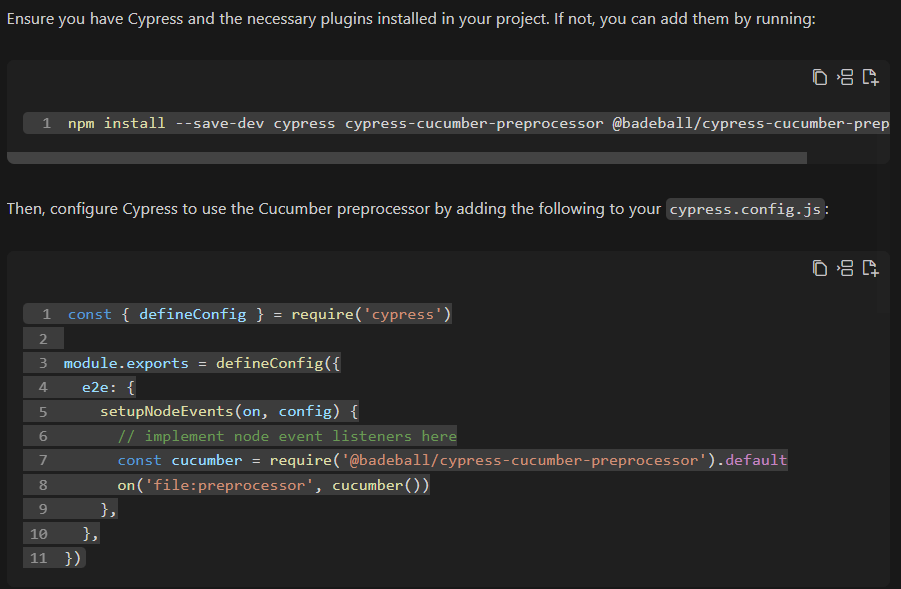
Finally, the information needed to install and set up the project’s dependencies in the index.js and cypress.json files was provided.
Watch the video tutorial on YouTube:
Conclusion
The purpose of ATDD is to encourage greater collaboration between all those involved in developing a product, resulting in a clearer understanding of the requirements that will be developed during a sprint. Furthermore, it contributes to a gradual increase in automated test coverage because new tests will be implemented as new features are delivered.
However, the automated acceptance tests must be ready before the functionality is tested. That’s when StackSpot AI becomes an outstanding alternative for speeding up the implementation of these tests, reducing QA coding time.
In addition to the test scenario code, StackSpot AI provides all the steps needed to install and set up the project’s dependencies, guiding the QA on how to structure the code according to the documentation and standards of the testing framework that was adopted.
Therefore, combining ATDD with StackSpot AI to build acceptance tests can be a good strategy for reducing coding time and effort and guaranteeing a more consistent and superior quality outcome, according to the company’s pre-determined standards.
References
- Acceptance Test-Driven Development (ATDD), step by step – InfoQ
- Acceptance Test Driven Development (ATDD) – Agile Alliance
- About StackSpot AI | StackSpot AI Documentation
- ATDD by Example: A Practical Guide to Acceptance Test-Driven Development by Markus Gärtner
- Agile Quality Journey: Apply early-cycle quality techniques for continuous software deployment by Antônio Muniz and others.
- StackSpot AI: Key Concepts | StackSpot AI Documentation
- StackSpot AI: hyper-contextualized code generation – StackSpot Blog

 Skip to content
Skip to content


